Led by BGS scientists Evi Petavratzi, Gus Gunn and Carolin Kresse, the Cobalt Commodity Review draws together a range of geological and market data to examine the global geological availability, extraction and supply of cobalt, highlighting areas that are current and crucial to a future low- carbon society.
Led by BGS scientists Evi Petavratzi, Gus Gunn and Carolin Kresse, the Cobalt Commodity Review draws together a range of geological and market data to examine the global geological availability, extraction and supply of cobalt, highlighting areas that are current and crucial to a future low- carbon society.
Cobalt is one of the essential metals for our modern world and is fundamental to our efforts to tackle climate change.
It already powers our mobile phones, tablets and laptops. This alone makes it a valuable metal, but the electrification of our energy systems and the future of electric vehicles means we will rely heavily on metals like cobalt to develop a low-carbon society.
It is cobalt’s use in the creation of rechargeable car batteries that continue to make it a fiercely competitive commodity for the international market.
The report by the BGS offers a review of current global resources and reserves, providing geological insight into supply routes, the potential of deep-sea mining for cobalt, extraction methods, processing technologies and the global cobalt supply chain.
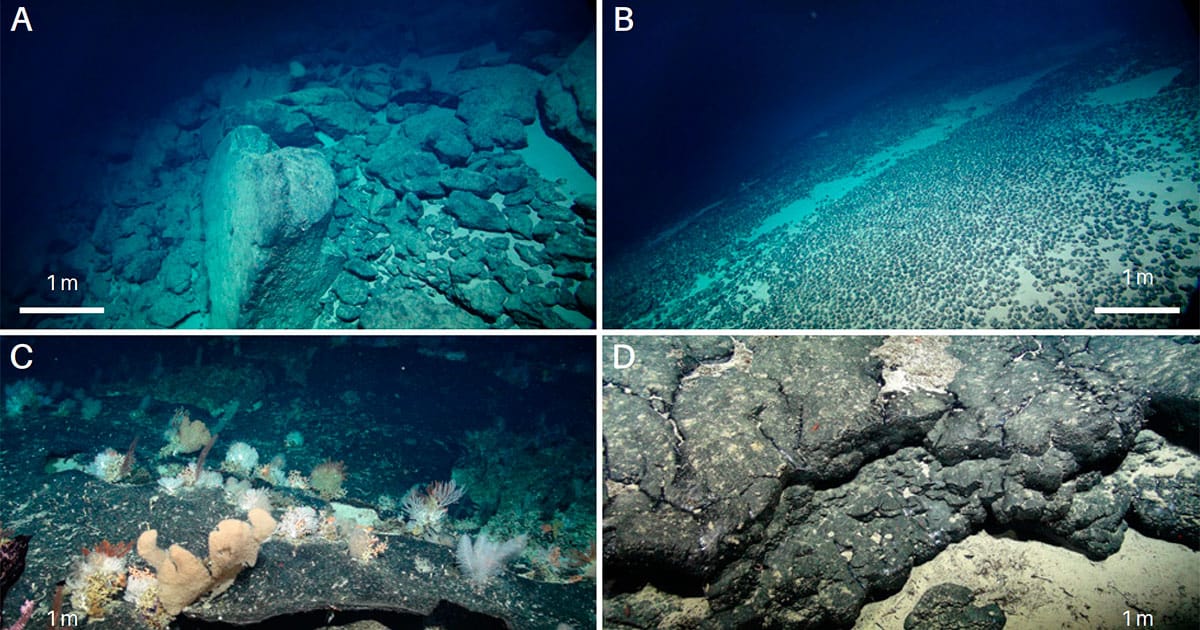
Relative to Earth’s crust, polymetallic nodules are strongly enriched in nickel, copper, cobalt and a range of other metals. These nodules are one of the primary targets for proposed ocean mining enterprises and it has been reported that the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ) alone contains 21 billion tonnes of nodules with a cobalt content of 44 million tonnes, which is 5.5 times larger than land-based cobalt reserves.
Evi Petavratzi, said: “Finding and protecting the resources required to sustain and meet our future needs will be critical over the coming decades, yet questions remain about how demand for cobalt can be satisfied under the current market conditions.
“The report reviews issues related to the responsible sourcing and sustainability of cobalt supply. Whilst it doesn’t set out to resolve these challenges, it brings together a wide range of globally reliable sources to provide a review of current market conditions and the implications for future supply.”
Cobalt is typically extracted as a by-product of other metal mining activity, mostly copper or nickel. It is now fundamental to modern industry and is classed by the EU and the US as a critical raw material.
Apart from being widely used in rechargeable batteries, cobalt is used to produce alloys that are extremely tough, anticorrosive and heat resistant under intense temperatures. The alloys are found in aircraft engines, nuclear power stations, turbines, cutting tools and even prosthetic limbs.
The use of cobalt in pigments to deliver a vivid blue color is another longstanding application. It even benefits our healthcare, as gamma rays from cobalt therapy enable radiotherapy treatment to be delivered very precisely in high doses.
While this has made cobalt extremely valuable to many industries, it is vehicle makers who will likely need the most dramatic increase in supply.
Around 50 per cent of cobalt demand is now for battery use. Based on the International Energy Agency cobalt demand projections, a threefold increase in global cobalt production is required by 2030 to satisfy the electric vehicles market alone. How we deal with this in a sustainable manner has geological implications and is just one area highlighted in the report.